|
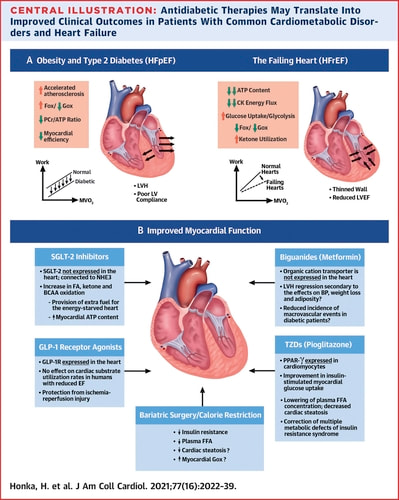
Therapeutic Manipulation of Myocardial Metabolism: JACC State-of-the-Art Review Henri Honka, Carolina Solis-Herrera, Curtis Triplitt, Luke Norton, Javed Butler, and Ralph A. DeFronzo J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021 Apr, 77 (16) 2022–2039 Abstract The mechanisms responsible for the positive and unexpected cardiovascular effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes remain to be defined. It is likely that some of the beneficial cardiac effects of these antidiabetic drugs are mediated, in part, by altered myocardial metabolism. Common cardiometabolic disorders, including the metabolic (insulin resistance) syndrome and type 2 diabetes, are associated with altered substrate utilization and energy transduction by the myocardium, predisposing to the development of heart disease. Thus, the failing heart is characterized by a substrate shift toward glycolysis and ketone oxidation in an attempt to meet the high energetic demand of the constantly contracting heart. This review examines the metabolic pathways and clinical implications of myocardial substrate utilization in the normal heart and in cardiometabolic disorders, and discusses mechanisms by which antidiabetic drugs and metabolic interventions improve cardiac function in the failing heart. Highlights • Bioengineering of cardiac metabolism represents a novel strategy to improve cardiac function and slow the progression of myocardial disease. • Modification of myocardial metabolism by SGLT-2 inhibitors, GLP-1 RAs, and pioglitazone can reduce CV events in patients with type 2 diabetes. • The potential benefit of shifting fuel utilization pathways in patients with HF should be investigated in future trials. SGLT-2i和 GLP-1 RA在2型糖尿病患者中產生積極心血管保護作用的機制仍有待確定。這些抗糖尿病藥物之有益心臟作用可能是因改變心肌代謝所引導的。常見的代謝異常,包括代謝(胰島素阻抗)症候群和2型糖尿病,與心肌基質利用率和能量傳遞的改變有關,而導致易患心臟病。因此,衰竭的心臟的特徵在於基質之糖分解和酮氧化的轉變,產生更多高能量,以合乎衰竭的心肌需求。 重點摘要: 1、心臟代謝的生物工程學顯示一種改善心功能並減慢心肌疾病進展的新策略。 2、SGLT-2i,GLP-1 RA對心肌代謝的改變可以減少2型糖尿病病患者的心血管事件。 3、將來的試驗中應研究改變燃料利用途徑對心衰竭患者的潛在益處。 Metformin與心臟 臨床實驗,降低患有心血管疾病的重大不良心血管事件。(但臨床試驗者較少) 此部分可能還需要更多臨床受試者來提供數據。 Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)與胰島素阻抗症候群 臨床實驗,降低患有心血管疾病併有第二型糖尿病的重大不良心血管事件。 藉由改善左心室舒張漢收縮功能、改善胰島素刺激的葡萄糖吸收以及降低脂毒性並增加支防氧化。 SGLT-2i,(Thrifty Substrate Hypothesis) (包括 empagliflozin,canagliflozin和dapagliflozin) 臨床實驗,降低患有心血管疾病併有第二型糖尿病的重大不良心血管事件,也降低心衰竭的風險。 對於非第二型糖尿病併有心臟衰竭是指左心室射出率低下的的住院風險也有所降低。. 由於目前僅是假說,所以還等待更多醫學臨床的實證。 (可能是酮生成與心肌對酮的吸收變強,進而改善心肌功能) GLP-1 RA(包括 liraglutide, semaglutide, dulaglutide, 及 albiglutide)和心臟保護 臨床實驗,降低患有心血管疾病併有第二型糖尿病的重大不良心血管事件,也降低心衰竭的風險。 GLP-1 RA主要可防止缺血再灌注損傷,也可增加心跳,可歸因於刺激竇房結。如果心跳加快是由副交感神經刺激引起的,則可能是GLP-1 RA類對心臟的保護作用。 減肥手術/熱量限制 由於在現實中實現長期的飲食熱量限制是非常難,因此減肥手術後的結果雖然是初步的,但仍需進行長期的研究,以檢查手術引起的體重減輕對心功能和心衰竭的影響。 更詳細內容 於專業人員區。
資料來源: J Am Coll Cardiol 2021, 77(16) 2022-2039
0 評論
發表回覆。 |
依主管機關相關規定,專業醫藥資訊僅提供醫藥專業人員參考(請申請核可通過後,即可閱讀專業人員區)。
恕不對外開放非專業人士使用。 每月文章
一月 2023
類別 |
營業時間:週一至週日(全年無休) 早上九點至晚上十一點四十分 (09:00~23:40)
|
地址:台北市松山區饒河街204號
|
聯絡我們 |

 RSS 訂閱
RSS 訂閱
